

Residential lawns and city parks), irrigation, and rainfall can carry
Grown or in areas with landscaping (including grassy areas of Metals, dirt, salts, and other toxic materials. Parking lots, streets, and roads where stormwater picks up oils, grease, Nonpoint sources of pollution in urban areas may include People can contribute to nonpoint-source pollution without even Substances can be hazardous to human health and aquatic life. Nutrients, microorganisms, and other toxic These are allĮxamples of pollutants released from nonpoint sources. To contain small amounts of lawn chemicals, oil, grease, gasoline,Īnd even residues from recent highway de-icing. Soil and clay particles from nearby construction, but also is likely

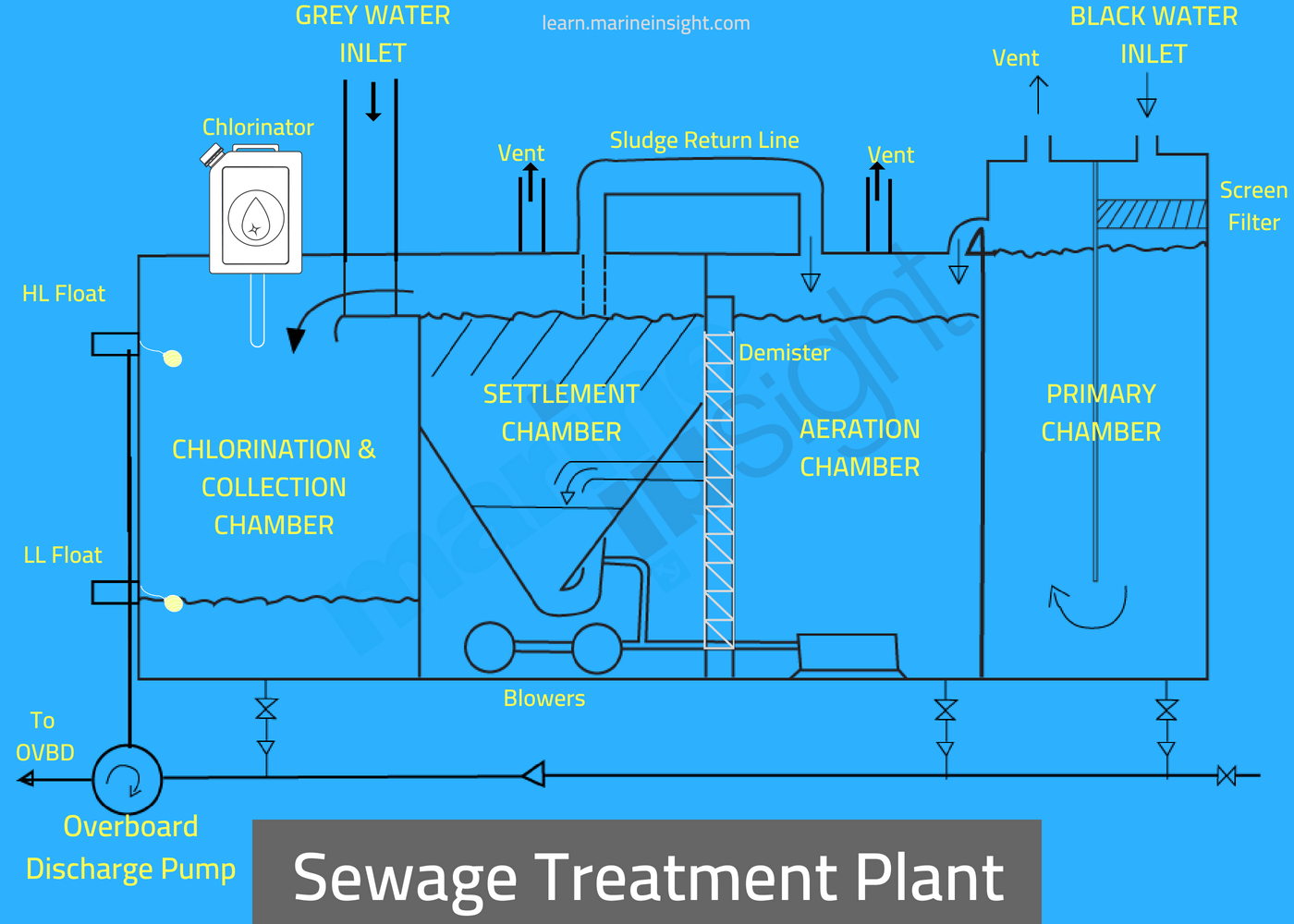
This silt-laden runoff from a residential area contains not only Through the ground with infiltrating rainwater, or direct discharges The end of a pipe to surface water, discharges on the ground that move If the facility or operator does not handle, store,Īnd dispose of the raw materials and wastes properly, these pollutantsĬould end up in the water supply. Raw materials used in the process as well as in theįor the facility. Landfills, utility stations, motor pools, and fleet maintenanceįor all of these activities, hazardous materials may be included in the Municipal point sources might include wastewater treatment plants, Mixing, and cleaning areas for pesticides, fertilizers, and petroleum. Operations, animal waste treatment lagoons, or storage, handling, Point sources of pollution from agriculture may include animal feeding Such as solvents, petroleum products (such as oil and gasoline), or The raw materials and wastes may include pollutants Manufacturing or maintenance, and then discharge various wastes from Types of business, industry, agricultural, and urban sources thatĬommercial and industrial businesses use hazardous materials in Types of point-source pollutants found in waters are as varied as the (such as the end of a pipe or an underground injection system) andĭiminishing concentrations farther away from the source. That has the highest concentrations of the pollutant nearest the source Water is stored in a lagoon and native plants, bacteria, algae, and small zooplankton filter nutrients and small particles from the water.Point-source pollutants in surface water and groundwater are usually Lagooning is another method for removing nutrients and waste from sewage. Nitrogen can also be removed using nitrifying bacteria. When the biomass accumulated in these bacteria is separated from the treated water, these biosolids have a high fertilizer value. In this process, specific bacteria, called polyphosphate accumulate organisms that store phosphate in their tissue. Phosphorus can be removed biologically in a process called enhanced biological phosphorus removal. These can disrupt the nutrient balance of aquatic ecosystems and cause algae blooms and excessive weed growth. Wastewater may still have high levels of nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus. Sand filtration, where water is passed through a sand filter, can be used to remove particulate matter. Several methods can be used to further disinfect sewage beyond primary and secondary treatment. Tertiary treatment (sometimes called “effluent polishing”) is used to further clean water when it is being discharged into a sensitive ecosystem. Figure: Diagram of Sewage Treatment Process: Sewage passes through primary, secondary, and tertiary treatment. Sewage treatment is done in three stages: primary, secondary and tertiary treatment. Blackwater comes from toilets and contains human waste. Greywater is water generated from domestic activities such as laundry, dishwashing, and bathing, and can be reused more readily. The separation and draining of household waste into greywater and blackwater is becoming more common in the developed world. In many areas, sewage also includes liquid waste from industry and commerce. It includes household waste liquid from toilets, baths, showers, kitchens, sinks, and so forth that is disposed of via sewers. Sewage is generated by residential and industrial establishments. aerobic: Living or occurring only in the presence of oxygen.zooplankton: Small protozoa, crustaceans (such as krill), and the eggs and larvae from larger animals.Effluent: Sewage water that has been partially treated and is released into a natural body of water a flow of any liquid waste.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
